| There exist formulas that can help find the exact values
of trigonometric functions without a calculator. sin
(u + v) = sin u cos v + cos u sin v
sin (u – v) = sin u cos v – cos u sin v
cos (u + v) = cos u cos v – sin u sin v
cos (u – v) = cos u cos v + sin u sin v
tan (u + v) = (tan u + tan v)/(1 – tan u tan v)
tan (u – v) = (tan u – tan v)/(1 + tan u
tan v)
These formulas can be applied in the evaluation of
a trigonometric function:
Find the exact value of sin 75°
sin 75° = sin (30° + 45°)
sin 75° = sin 30° cos 45° + cos 30°
sin 45°
sin 75° = (1/2) (rt(2)/2) + (rt(3)/2)(rt(2)/2)
sin 75° = (rt(2) + rt(6))/4
Find the exact value of cos (p/12)
cos (p/12) = cos (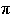 /3
– /3
– 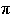 /4) /4)
cos (p/12) = cos (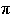 /3)
cos ( /3)
cos (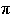 /4)
+ sin ( /4)
+ sin (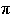 /3)
sin ( /3)
sin (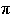 /4) /4)
cos (p/12) = (1/2) (rt(2)/2) + (rt(3)/2) (rt(2)/2)
cos (p/12) = (rt(2) + rt(6))/4
Also, one can apply the sum and difference formulas
in reverse so to speak:
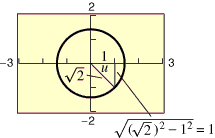
Find the exact value of sin (u – v) so that
cos u = 1/rt(2) where 3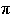 /2
< u < 2 /2
< u < 2 and sin v = 3/5 where
and sin v = 3/5 where  /2
< v < /2
< v < 
cos u = 1/rt(2) and u is in the fourth quadrant. That
means that sin u = – 1/rt(2)
sin v = 3/5 and v is in the second quadrant. That means
that cos v = – 4/5
If sin (u – v) = sin u cos v – sin v cos
u then
sin (u – v) = (– rt(2)/2) (– 4/5)
– (3/5) (rt(2)/2)
sin (u – v) = (4 rt(2))/10 – (3 rt(2))/10
sin (u – v) = rt(2)/10
|